Finishing
- Wide range of post-processing
- Customized solutions based on special requirements
- Improve the appearance and protection
Post-processing is an important step for some parts to be used in special conditions. It is the process of finishing the part to the desired surface quality and dimensional accuracy. Post-processing operations can be performed manually or automatically, and can include a variety of processes, such as anodizing, heat treatment, passivation, polishing, blasting, coating.
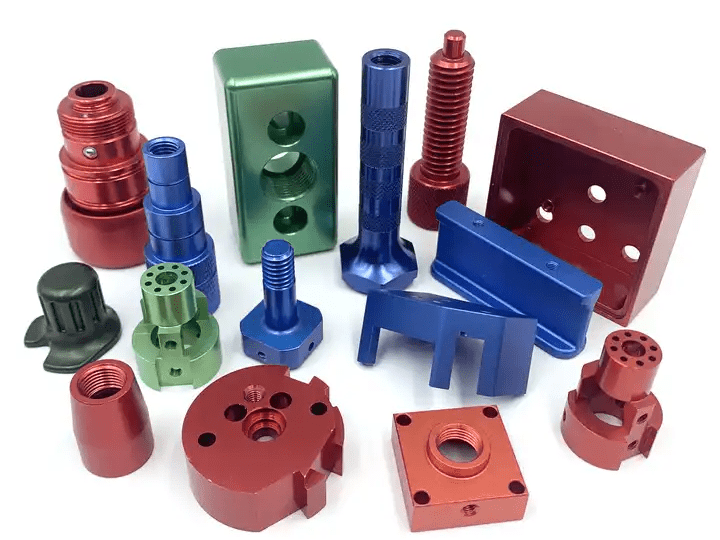
Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the aluminum surface into a hard, durable, and corrosion-resistant layer of aluminum oxide. The anodizing process is environmentally friendly and produces a non-toxic and non-flammable finish.
There are two main types of anodizing:
- Type II anodizing: Type II anodizing is the most common type of anodizing and is used for a wide variety of applications. Type II anodizing produces a thin, transparent layer of aluminum oxide that is typically 5-25 micrometers thick.
- Type III anodizing: Type III anodizing, also known as hard anodizing, is used for applications where increased wear and corrosion resistance is required. Type III anodizing produces a thicker layer of aluminum oxide that is typically 25-100 micrometers thick.
Anodizing offers a number of benefits, including:
- Improved corrosion resistance: Anodized aluminum is highly resistant to corrosion from atmospheric exposure, salt spray, and chemicals.
- Increased wear resistance: Anodized aluminum is harder than bare aluminum and is therefore more resistant to wear and abrasion.
- Improved electrical insulation: Anodized aluminum is a good electrical insulator and can be used to create electrical components, such as capacitors and resistors.
- Decorative finishes: Anodizing can be used to create a variety of decorative finishes, such as clear, matte, and colored finishes.

Heat treatment
Heat treatment is a process of heating and cooling a material to change its properties. Heat treatment can be used to improve the strength, hardness, toughness, ductility, and wear resistance of a material. Heat treatment is used in a wide variety of industries, including manufacturing, construction, and aerospace.
Benefits of Heat treatment: improved strength, increased hardness, improved toughness, improved ductility, improved wear resistance, improved corrosion resistance

Passivation
Passivation is a chemical process that removes surface contaminants and creates a thin, protective layer on the surface of a metal. This layer is typically made of chromium oxide, which is a very stable and corrosion-resistant material. Passivation is commonly used on stainless steel, but can also be used on other metals, such as aluminum and titanium.
Benefits of passivation
- Improved corrosion resistance: The chromium oxide layer created by passivation is very resistant to corrosion from atmospheric exposure, salt spray, and chemicals.
- Reduced contamination: Passivation can help to reduce the contamination of the metal surface, which can be important for applications in the food and beverage and pharmaceutical industries.
- Improved appearance: Passivation can improve the appearance of the metal surface by giving it a brighter and more uniform finish.

Polishing
Let's make something significant today!
- Polishing is a surface finishing process that uses abrasive materials to smooth and refine the surface of a material. Polishing can be used to improve the appearance, performance, and durability of a material. Polishing is used in a wide variety of industries, including manufacturing, construction, and electronics.
There are two main types of polishing:
- Mechanical polishing: Mechanical polishing uses abrasive tools, such as wheels, belts, and brushes, to remove material from the surface of the material.
- Chemical polishing: Chemical polishing uses acids or other chemicals to etch the surface of the material and remove imperfections.
Benefits of polishing:
- Improved appearance: Polishing can give a material a bright, shiny finish.
- Improved performance: Polishing can improve the performance of a material by reducing friction and wear.
- Improved durability: Polishing can improve the durability of a material by making it more resistant to corrosion and abrasion.


Balsting
Blasting is a process of cleaning, shaping, or roughening a surface by propelling a stream of abrasive material at high velocity against it. Blasting can be used on a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and concrete.
Abrasive blasting is the most common type of blasting and is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Surface cleaning: Abrasive blasting can be used to remove dirt, rust, paint, and other contaminants from a surface.
- Surface preparation: Abrasive blasting can be used to prepare a surface for painting, coating, or other finishing processes.
- Surface roughening: Abrasive blasting can be used to roughen a surface to improve its adhesion properties.
- Surface shaping: Abrasive blasting can be used to shape a surface by removing material from specific areas.
Blasting offers a number of benefits, including:
- Effective cleaning: Blasting can be used to remove even the most stubborn contaminants from a surface.
- Versatile: Blasting can be used on a variety of materials and for a variety of purposes.
- Efficient: Blasting can be a very efficient way to clean or shape a surface.
- Cost-effective: Blasting is a relatively cost-effective process.

Coating
Coating is the process of applying a thin layer of material to the surface of another material. Coatings can be used to protect, decorate, or enhance the performance of the substrate material. Coatings are used in a wide variety of industries, including manufacturing, construction, and transportation.
There are many different types of coatings, each with its own specific properties and benefits. Some of the most common types of coatings include:
- Paints: Paints are a type of coating that is used to protect and decorate surfaces. Paints are typically made of a pigment, a binder, and a solvent.
- Enamels: Enamels are a type of coating that is similar to paint, but they are more durable and resistant to chipping and scratching. Enamels are often used on appliances and other metal products.
- Powders: Powders are a type of coating that is applied to a surface as a dry powder and then cured using heat or UV light. Powder coatings are very durable and resistant to corrosion.
- Plastics: Plastic coatings can be used to protect surfaces from corrosion, abrasion, and other forms of damage. Plastic coatings are often used on automotive parts, electronic components, and medical devices.
- Metals: Metal coatings can be used to protect surfaces from corrosion, abrasion, and other forms of damage. Metal coatings are often used on automotive parts, aircraft components, and industrial equipment.
Coatings offer a number of benefits, including:
- Protection: Coatings can protect surfaces from corrosion, abrasion, wear and tear, and other forms of damage.
- Decoration: Coatings can be used to improve the appearance of surfaces by giving them a specific color, finish, or texture.
- Performance: Coatings can be used to enhance the performance of surfaces by improving their electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, or other properties.
Coatings are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Manufacturing: Coatings are used to protect and decorate a wide variety of manufactured products, such as automotive parts, aircraft components, and electronic devices.
- Construction: Coatings are used to protect and decorate a variety of building materials, such as concrete, steel, and wood.
- Transportation: Coatings are used to protect and decorate a variety of transportation vehicles and equipment, such as cars, trucks, airplanes, and ships.
